Radio Program
Our regular Science and the SeaTM radio program presents marine science topics in an engaging two-minute story format. Our script writers gather ideas for the radio program from the University of Texas Marine Science Institute's researchers and from our very popular college class, Introduction to Oceanography, which we teach to hundreds of non-science majors at The University of Texas at Austin every year. Our radio programs are distributed at to commercial and public radio stations across the country.
Ghosts haunt the oceans. They scuttle along the shore, lurk among the corals, and glide through the dark ocean depths. Some of them blend into the shimmering water so completely that they’re almost invisible. Others stare with big, dark eyes, watching every move as they slide through the water.
None of the ghosts are apparitions from the afterlife, though -- well, almost none of them. Instead, they’re fish and shellfish found around the world. But they’re called ghosts because they have some spirit-like qualities.
In late 2011, Hawaiian surfer Garrett McNamara took a thrilling ride -- or a chilling one, depending on your perspective. He surfed a wave as tall as a seven-story building. That earned him a spot in the Guinness Book of World Records. But both McNamara and another surfer say they’ve ridden even taller waves since then -- and at the same spot: near the village of Nazaré, Portugal.
Until the record-setting performance, Nazaré was little known. Since then, however, it’s become a magnet for big-time surfers and those who just want to be thrilled by the view.
Modern-day scorpions are small but creepy, and the stingers on their tails pack a painful punch. Some of their ancient relatives were also creepy, but they were big, and their tails may have packed a deadly punch.
Sea scorpions first appeared almost 470 million years ago -- one of the first big predators in the oceans. They stuck around for more than 200 million years. The first of these creepy critters lived in warm, tropical oceans and seas around the world. Later ones inhabited the oceans, marshes along the coast, freshwater lakes, and other wet environments.
A red tide can cause all kinds of problems. Neurotoxins in the microscopic organisms that cause red tides can contaminate oysters and other shellfish. Anyone who eats the shellfish can get sick, or even die. So it’s important to know when one of these harmful algal blooms is developing -- early detection can keep people from getting sick.
Sea urchins have some of the best defense mechanisms around. Sharp spines jab any predators that try to grab them. And tiny, venomous fangs on the end of long stalks snap at the predators.
One species of urchin adds one more layer of defense. It can launch hundreds of the little fangs into the water around it. That creates a defensive screen that helps keep the predators at bay.
The collector sea urchin is found in warm, shallow waters at several locations around the world. It’s most common in Australia, especially on the Great Barrier Reef.
The algae octopus uses an elaborate camouflage scheme to stay safe. It can change the color and shape of structures on its body and arms to make it look like an algae-covered shell.
When that doesn’t work, though, it has another defense mechanism: Run! It can hoist its body on two of its eight arms and skedaddle, running as fast as it can swim. In fact, it’s one of only two species of octopus that’s known to run on two “legs.”
Ocean creatures don’t have to be big to be loud. One of the loudest of all is only a couple of inches long. But it produces “bangs” that are louder than a gunshot. And biologists are just beginning to study what makes them pop off.
Snapping shrimp are found in coral and rocky reef systems around the world. They look like tiny lobsters, with one claw that’s much bigger than the other.
A small crab in Japanese waters has a pattern on its back that looks like the face of a fearsome samurai. Legend says the crabs are the reincarnated spirits of warriors of the Taira clan, who drowned themselves to avoid capture more than 800 years ago. Today, the scientific name for the crabs honors the warriors: Heikeopsis japonica -- the Japanese Taira clan.
The doctorfish sounds like it should scurry from reef to reef, healing other fish along the way. In reality, though, the name tells us that the fish is dangerous: It can inflict nasty cuts on rivals and predators using two “scalpels” on its sides.
The doctorfish grows up to about 15 inches long, and can weigh up to about 10 pounds. It has a tall, flat body that’s blue-gray or brown, with vertical stripes on its sides.
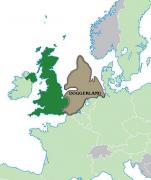
A sand bank in the North Sea, between Great Britain and Denmark, has long been a popular fishing ground. Dutch vessels, known as doggers, plied the shallow waters above the bank for cod as early as the 14th century. But others were gathering food there thousands of years earlier -- not by fishing, but by hunting for deer and other animals.
The bank is known today as Dogger Bank, after the Dutch boats. It was the highest region of what’s known as Doggerland -- a land bridge that connected Great Britain to the European mainland during the last ice age.